As the world races to meet the insatiable computing demands of artificial intelligence (AI), one thing is becoming increasingly clear: the future of networking may rest on a humble but evolving foundation: Ethernet.
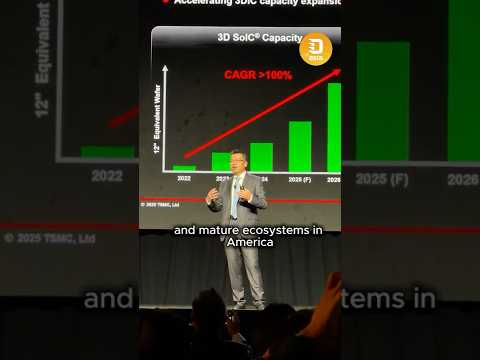
TSMC will build two advanced packaging plants in Arizona, part of a sweeping expansion to support soaring demand for AI chips and solidify its strategic presence in the US, Chairman and CEO C.C. Wei announced during the company's latest earnings call.