Technology has always played an important role in improving the quality of people's lives. However, not all technological advances are needed. A study on the human history will tell us what people are mainly pursuing is freedom and security. In a recent interview, Jiu-Fan Lin, sales vice president, AMobile Intelligent, gave his fresh point of view - NB-IoT is a new technology shaped to human needs.
"We want young people to live harder and embrace endless possibilities enabled by technology," noted Lin as he thinks many technological innovations were created because people started to think about how to build safer and more livable cities after being hit by devastating natural disasters. After years of refinement, NB-IoT is not only an enabler of smart cities but more importantly a new hope for higher quality of life.
NB-IoT brings people closer to their surroundings
Taiwan has experienced major natural disasters, such as the 921 earthquake and Typhoon Nari. "If there had been a system to warn the Taipei City authorities that the flood gates were left open, maybe we could have prevented Typhoon Nari from causing the widespread flooding in Taipei," indicated Lin. If we had been able to use IoT sensors for early warning at the time of Typhoon Nari, we might have avoided the extensive damage.
NB-IoT communication technology can be used in wide-ranging applications not only for early warning purposes but also for keeping track of the changes in the city's natural environment, for example, monitoring water levels and river flows. Such types of natural environment monitoring do not need to collect data at the rate of hundred times per second as the natural environment generally does not change at a rapid pace and the monitoring system can be configured to collect and report data at an interval of a few times per month or per year. According to Lin, using NB-IoT for effective wide-area management and monitoring in city administration helps people achieve the desired quality of life and prevent disasters.
AMobile Intelligent and MediaTek have combined forces to develop NB-IoT modules, which are powered by MediaTek's NB-IoT chips purposed-built for AMobile Intelligent's products, including water monitoring, water meter, traffic and smart home solutions. In particular, its NB-IoT solution has been put to use to monitor India's Ganges River and Thailand's Mekong River.
Built on top of 3GPP standards, NB-IoT has deployment cost advantages
Major cities around the globe are endeavoring to become smart cities by actively deploying IoT devices citywide. However, with a wide variety of devices being put to use for different applications and cloud infrastructure for collecting and analyzing data being in place, equipment enabling the connection of massive devices, long-range and low-power data transfer and low deployment cost is not yet available, so full-scale IoT realization still has "one last mile" to go.
NB-IoT is what it takes to complete the last mile. NB-IoT enables low-power wide-area communication and can operate with the cellular network structure of most telecom operators' base stations. In other words, manufacturers of NB-IoT solutions only need to focus on the designs and functions of their products without having to worry about infrastructure issues.
Based on 3GPP standards, NB-IoT can make use of most existing base stations and upgrade them to serve as media for data transfer. Compared to LoRa and Sigfox using unlicensed frequency bands, NB-IoT has superior advantages.
However, compared to LTE-M, also transmitting signals through telecom operators' base stations, NB-IoT is more favored because NB-IoT chips have lower cost and higher performance and support over-the-air (OTA) upgrade, according to market research reports. These benefits have allowed NB-IoT to surpass LTE-M in a short time and likely to outperform Sigfox and LoRa in five years in terms of market demand.
According to Lin, NB-IoT sends data through 4G networks and will use 5G networks in the future. Take the current 4G networks for example. NB-IoT uses fragmented 4G frequency bands for data transfer, so service providers or general users pay smaller fees than mobile subscription charges. For advanced technologies to become widespread in people's lives, they have to enable access by everyone. If businesses can reduce their operating costs, they will be able to pass the savings to their customers.
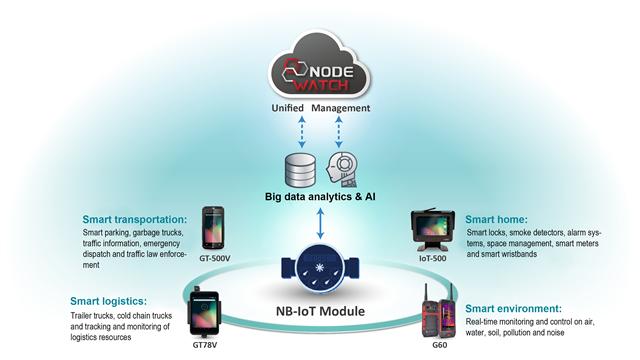
Current applications of AMobile Intelligent's NB-IoT modules

Jiu-Fan Lin, sales vice president, AMobile Intelligent
DIGITIMES' editorial team was not involved in the creation or production of this content. Companies looking to contribute commercial news or press releases are welcome to contact us.