According to the latest Taiwan Cancer Registry published by the Ministry of Health and Welfare (MOHW) in November 2023, lung cancer has overtaken colon cancer as the most common type of cancer in Taiwan. It is also one of the leading causes of death around the world. One of the reasons that lung cancer has such a high mortality rate is that it is often only diagnosed in later stages when the best time for treatment has lapsed. Therefore, early screening is of utmost importance. The DeepLung-CAC developed by DeepRad.AI employs multimodal AI technology, utilizing low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) imaging It aims to achieve the goal of preventive medicine by detecting lung nodules and simultaneously predicting the risks of coronary artery calcification.
DeepRad.AI is a spin-off company of Taipei Medical University founded by the university's former president, Professor Cheng-Yu Chen, a specialist in AI research. The company's research and development are centered on reducing case fatality rates through early detection and prevention, aiming to optimize the utilization of healthcare resources in society. Yao-Chi Chang, the CEO of DeepRad.AI, emphasized that the earlier lung cancer is detected, the higher the chances of recovery. With conventional X-ray technology, locating nodules is challenging, and by the time symptoms are identified, the cancer often progresses to stages three or four, resulting in a survival rate of only 10-30%. The widely used LDCT is highly effective and capable of detecting stage one or even stage zero lung cancers, significantly boosting the survival rate to over 90%.
Nonetheless, the evaluation of LDCT lung cancer screening results currently relies on radiologists. The latest CT scanners can now offer up to 640 slices, resulting in a significant increase in the number of images for analysis. This surge in workload poses a substantial impact on doctors' productivity. In contrast, the DeepLung-CAC optimizes the clinical workflow to address these challenges.
According to Yao-Chi Chang, DeepLung-CAC can provide doctors with preliminary results within five minutes after the completion of the LDCT scan. The patient's old and new images can also be compared to identify any nodular changes, assisting the doctor in explaining the screening results to the patient. Furthermore, DeepLung-CAC can automatically generate lung cancer screening reports that align with the Health Promotion Administration (HPA) standard. This significantly reduces the time required by doctors for analysis and report generation, enhancing the accuracy of test results and overall productivity.
In addition to lung cancer screening, the DeepLung-CAC can simultaneously assess coronary artery calcification risks. Coronary artery calcification serves as a crucial indicator for evaluating the risk of cardiovascular disease. DeepRad.AI utilized paired data (i.e., examination data from simultaneous screening for lung cancer and coronary artery calcification)to train DeepLung-CAC. This enables the platform to simultaneously detect early-stage lung cancer and assess coronary artery calcification risk in a single LDCT scanning session. Following four years of research and analysis, DeepLung-CAC is now capable of screening for these two diseases, which rank as the first and second leading causes of death in Taiwan, using a single LDCT scan.
The platform is currently undergoing clinical trials in anticipation of TFDA approval, expected to be granted in 2024. Clinical trials are underway at Taipei Medical University Hospital and Shuang Ho Hospital, where the platform has demonstrated improved CT interpretation efficiency.
As for the market potential of DeepLung-CAC, approximately 500,000 people in Taiwan are categorized as high-risk for lung cancer, but only 50,000 underwent government-funded screening last year. If the concept of preventive health gains widespread acceptance, this could lead to a tenfold increase in overall screening volume in Taiwan. However, with only 1,600 radiologists currently available, there is an urgent need for AI to reduce their workload and enhance the quality of care. DeepRad.AI aims to assist and optimize the overall process for radiologists using AI. By improving the efficiency of lung cancer screening and early detection rates, the vision of successful lung cancer prevention and treatment can be realized.
DeepRad.AI has made progress in screening for lung cancer and coronary artery calcification. The next step is to proactively develop predictions for osteoporosis and dementia. The company aims to contribute to innovative breakthroughs in the fields of preventive health and diagnosis.
Yao-Chi Chang pointed out that the team's hard work and Taiwan's innovation-friendly environment are the two main factors to success. In addition to a focus on research and development, precise and effective market planning is crucial for start-ups to promote their products. He expresses hope that policy support from government agencies will attract the attention of foreign investors to DeepRad.AI's technology and platform, facilitating successful commercialization. Looking ahead, he envisions Taiwan refining its laws, regulations, and auxiliary policies to leverage its capabilities in technology and healthcare sectors, creating an even greater competitive edge in smart healthcare.
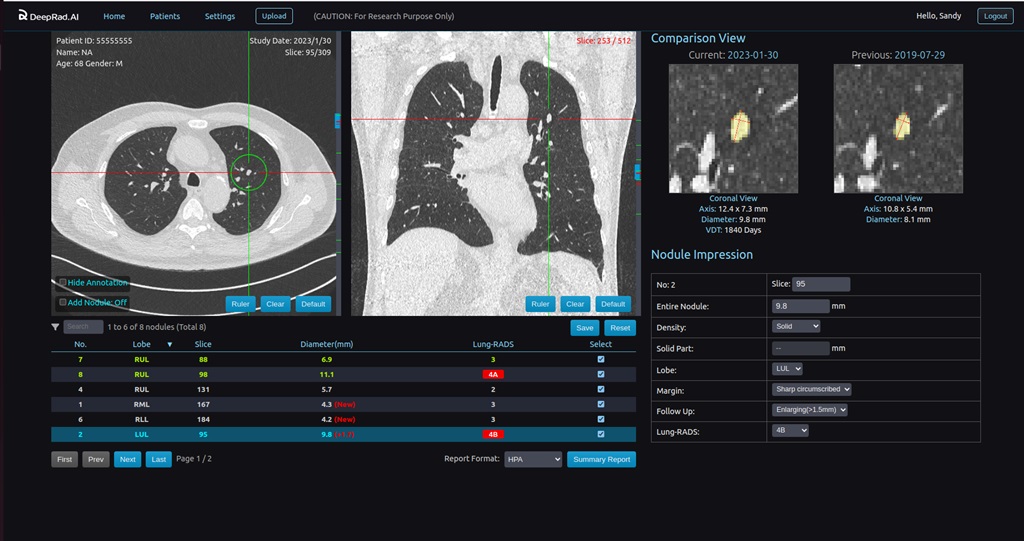
DeepRad.AI utilizes a single LDCT examination and multimodal AI technology to conduct a one-time scan of the lungs and heart, enabling automated lung nodule detection and prediction of coronary artery calcification risk. The examination concludes with a standardized text report for doctors' reference
Photo: Company
