As the epicenter of the magnitude 9.0 earthquake that struck off the coast of Japan on March 11, 2011 was located close to the northeastern prefecture of Miyagi, the local area has suffered catastrophic damage. But Miyagi is located some distance from the areas where Japan's panel industry is concentrated. As Japan's TFT LCD factories and component plants are mostly located in central and southern Japan, Digitimes Research believes the recent earthquake is not predicted to have a major impact on the majority of key panel component suppliers in Japan.
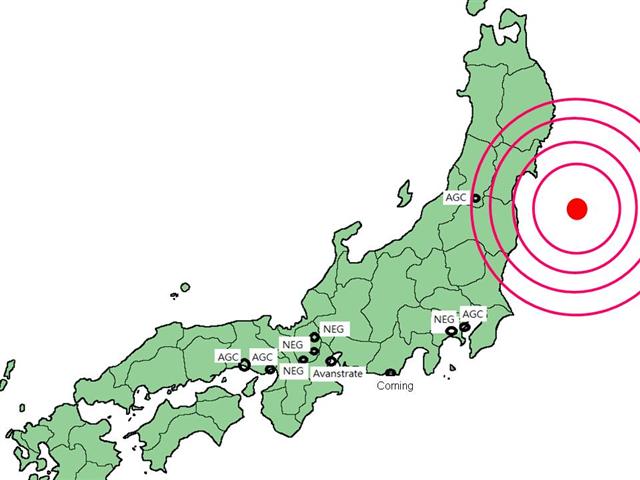
Factories located in areas where the magnitude of the earthquake was relatively high (5-lower or above, according to the JMA seismic intensity scale used in Japan) include the Asahi Glass (AGC) plant in Yonezawa; Hitachi and IPS Alpha's plants in Mobara, Chiba (3.8G, 4.5G and 6G); NEC's 3G plant in Akita; DNP and Toppan's old color filter (CF) production lines; Fujifilm's LCD optical film plant; and the former CF factory of Andes, which was subsequently reorganized under Japan's Civil Rehabilitation Law to become a glass touch sensor plant.
The more seriously affected TFT LCD panel factories include Hitachi and IPS Alpha's plants in Mobara, Chiba and NEC's 3G plant in Akita. But these facilities all essentially consist of older production lines. While Hitachi remains one of the main global suppliers, the majority of the other panel production lines have already been demoted to second or third tier plants. The earthquake is therefore not anticipated to have a major impact on global panel supplies.
Turning to glass substrates, Corning's Japan facilities and Asahi Glass (AGC) have been fortunate, as both have indicated that the earthquake has had little or no impact on their factories. Corning had already been forced to rely on Corning Taiwan's factories to supply glass substrates following stoppages at its Shizuoka plant caused by a previous earthquake.
The glass substrate factory hit hardest was the Asahi Glass (AGC) plant located in Yonezawa, Yamagata Prefecture, where seismic intensity was rated at 5-upper; however, production has not stopped at the plant. Asahi Glass has indicated that although the earthquake has resulted in production stoppages at its Kashima, Keihin and Chiba plants, there has been no major damage to any of the firm's own factories. Corning's factory in Shizuoka Prefecture was subjected to a seismic intensity of four; the company has indicated that the recent earthquake has had no effect whatsoever on this factory.
The earthquake may prove to have a more serious impact on TAC film, a key component of polarizers, as Fujifilm's polarizer TAC film plant in Minamiashigara, Kanagawa Prefecture is located in an area where the earthquake's intensity was rated at 5-lower (JMA scale). Japan's two largest manufacturers account for more than 90% of global TAC film supplies. However, as Fujifilm, the largest manufacturer, has significantly expanded capacity at its facilities in Kumamoto Prefecture on the island of Kyushu, and the number two supplier Konica Minolta has already completed the construction of its new factory in Kobe, the overall effect on supplies is still projected to remain within manageable levels.
Supply of anisotropic conductive film (ACF), which bonds driver ICs, has not seen much impact from the earthquake. Hitachi Chemical and Sony Chemicals account for a total of 90% of the global ACF market. Their major ACF facilities in Japan were not damaged in the quake but were temporarily shut down due to power outages. If power shortages prolong in Japan, their production may be affected.
It is worth noting that the earthquake may have a more serious impact on DNP's CF factory located in Kazo, Saitama Prefecture, where the earthquake's seismic intensity was rated at 5-lower. Toppan's CF factory in Niiza, Saitama Prefecture was also hit with a seismic intensity of 5-lower. Fujifilm's polarizer TAC film plant in Minamiashigara, Kanagawa Prefecture is located in an area hit with a seismic intensity of 5-lower, and may also be more seriously affected.
| Earthquake impact on Japan's LCD component industry | |
| Component | Impact |
| Panels |
The major panel factories are located far from the epicenter of the earthquake, and the overall effect has been small. Sharp's 8.5G and later generation TFT LCD panel factories have all been designed with enhanced earthquake protection.
|
| Glass substrate |
The two largest manufacturers Corning and AGC have indicated that there has been little or no impact on their facilities.
|
| Color filter |
As factories in many countries source color filters domestically, the global impact on this sector will be small.
|
| Optical film |
Fujifilm's TAC film plant in Minamiashigara, Kanagawa Prefecture was subjected to a relatively high seismic intensity. However, Fujifilm has significantly increased capacity at its other plants, which will reduce the impact on its supplies. Supply of ACF has not seen much impact.
|
Source: Digitimes Research, March 2011
The earthquake has little effect on glass substrate supplies from Corning and AGC
Source: Digitimes Research, March 2011