As the automotive industry continues its journey toward greater electronic integration, propelled by the dual forces of electrification and smart technology, the demand for automotive printed circuit boards (PCBs) is on the rise. According to DIGITIMES Research, the global automotive PCB market reached a valuation of US$9.07 billion in 2022, with projections indicating that it will exceed US$12.5 billion by 2027, marking a remarkable growth rate of 37.4% over a five-year period.
In line with Jessie Lin's insights from DIGITIMES Research, global electric vehicle sales approached the ten million mark in 2022 and are expected to soar beyond 40 million units by 2027, showcasing a substantial increase within this six-year timeframe.
Global automotive PCB market
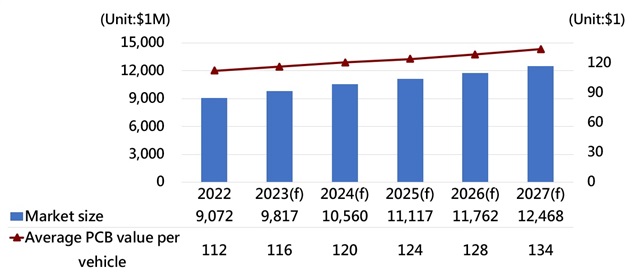
Source: TTM、DIGITIMES Research, September 2023
PCBs are primarily integrated into various electronic components of automotive systems, including power control and charging systems, safety control systems, vehicle electronics, in-car entertainment systems, and more. The escalating demand for automotive PCBs can be primarily attributed to the trends of electrification and smart technology, which have also led to enhancements in PCB technology and specifications. Consequently, the level of electronicization in automobiles is on the ascent with automotive electronics accounting for approximately 45% of the production cost per vehicle by 2027, up from 30% in 2020. The value of a single vehicle's PCB is expected to rise from US$112 in 2022 to US$134 by 2027.
In terms of electrification, the PCB area required for electric vehicle power systems has substantially increased in comparison to conventional petrol cars, necessitating compliance with high current and high voltage specifications. Consequently, the cost of a single vehicle's PCB is estimated to be around US$275, significantly higher than the US$70-90 range for traditional gasoline cars. Electric vehicles require robust copper plates capable of withstanding high voltage and current to enhance system efficiency.
The concept of smart technology denotes the automotive industry's progress toward Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) and even more advanced autonomous driving capabilities, combined with connectivity features. Meeting the demands of these functionalities necessitates the utilization of higher-density and higher-performance PCBs. Manufacturing processes often incorporate high-density interconnect (HDI) and high-frequency PCB technologies to accommodate the miniaturization of sensors, extensive data transmission, and low power consumption.
As the number of sensors integrated into vehicles increases, the need for PCBs follows suit. For instance, L4/L5 vehicles are equipped with over 30 sensors, a significant leap compared to the approximately 15 sensors used in L2 vehicles, underscoring the requirement for a greater number of PCBs to connect sensors to other electronic systems within the vehicle.
About the analyst
Jessie Lin received a master's degree from the Department of Business Administration at the National Taiwan University of Science and Technology. Her research focuses on automotive, LED, and display panels.

Credit: DIGITIMES


